What is Temperature Dependence of Resistivity Class 12
Temperature Dependence of Resistivity Can be understand by this popular equation .
ρ(T) = ρ₀[1 + α(T – T₀)]
here, ρ(T) = final resistivity at temp T
ρ₀ = final resistivity at temp T₀
α = thermal coefficient of resistivity
♦ α is +ve for conductor and -ve for semiconductor.
it means, For conductor, its resistivity increase with temperature
and for semiconductor , its resistivity decrease with temperature
Graph for conductor
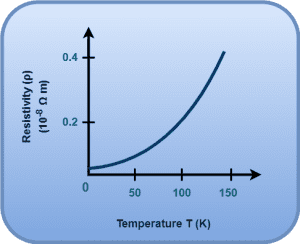
Graph for Semiconductor
![]()
♦ For nichrome and mangnine α = 0
it means on increasing temperature , its resistivity does not change
so nichrome and mangnine are used in the device, which works on the
heating effect of current .
Graph for nichrome and mangnine
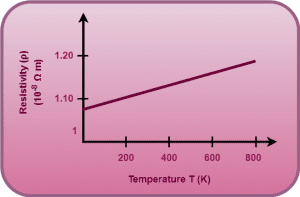
Resistivity of nichrome and mangnine change neglegibely
Note :- if we multiply the equation by l/A both side
then equation will be modify as
R(T) = R₀[1 + α(T – T₀)]
R= resistance , l = length of wire , A = cross-sectional area of wire .
Q.At room temperature (27.0 °C) the resistance of a heating element
is 100 Ω. What is the temperature of the element if the resistance is
found to be 117 Ω, given that the temperature coefficient of the
material of the resistor is 1.70 × 10–4 °C–1
solve this or watch this video. For detail on This Topic .
.